Control the temperature of your hot and cold products
Température
⏳ Temps de lecture : 5 min
? Mis à jour le : 12/03/2025
Summary
- Cold link definition
- What HACCP surveys should be carried out to guarantee food safety in cold or hot links?
- Cold link regulations: what does the law say?
- Product shelf life: what does the law say?
- Hot links definition
- Hot links regulation: what does the law say?
- What is the protocol for rethermalization in cold links?
- Cold links in central kitchens: how to go digital?
- Download your guide to cold and hot links in PDF
Cold link definition ❄️
We speak of cold link when the place of production is different from the place of consumption and the delivery between the 2 sites is made at temperature < 3 °C.
What are the different stages of the “liaison froide” process?
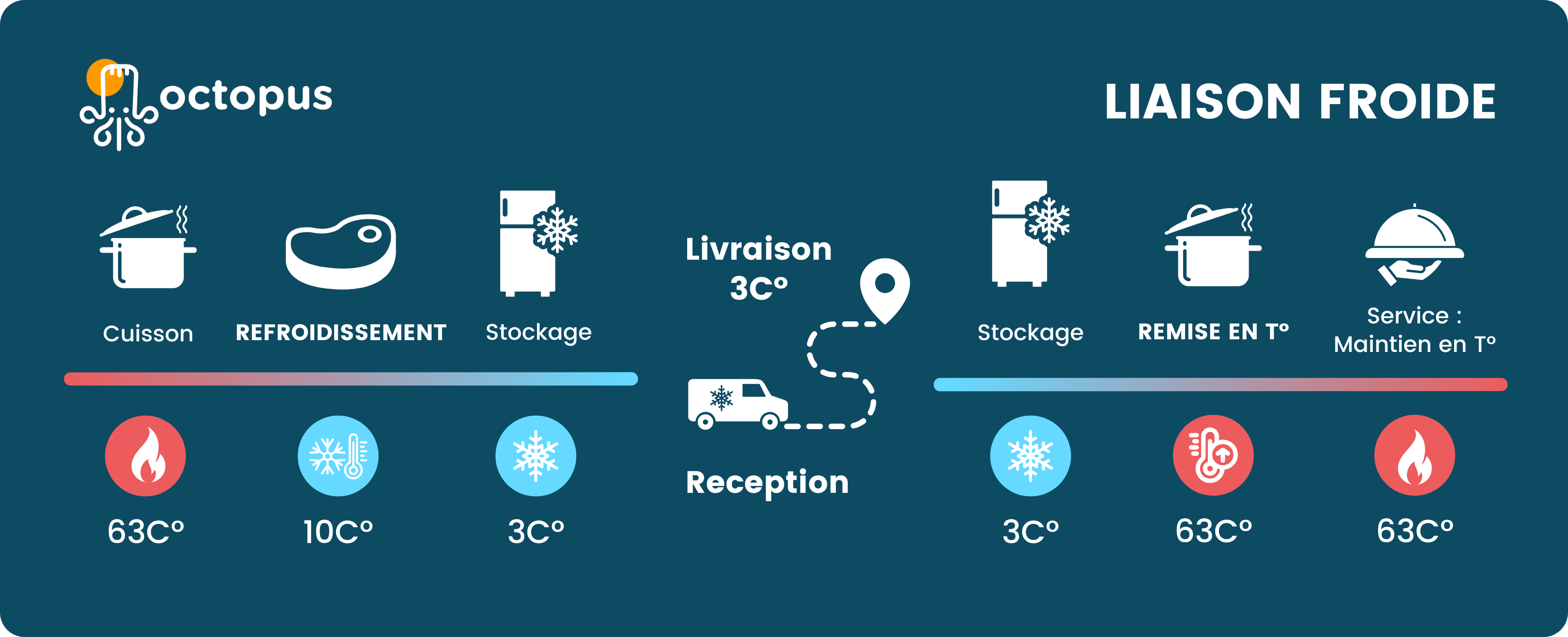
Cold link regulations: what does the law say?⚖️
You can download the Good Hygiene Practices Guide (GBPH) for Home Meal Delivery.
The HACCP method requires respecting the temperature range for rapid cooling for several reasons:
- Hygiene 🧼: the risk of microbial growth 🦠 is very high between 63°C and 10°C. Pathogenic bacteria are destroyed above 63°C, while below 10°C, their growth is stopped. Too slow cooling therefore increases the risk of contamination. ⚠️
- Organoleptic quality 🍽️: rapid cooling better preserves flavors, texture, and limits evaporation or oxidation. This is essential in pastry making for mousses, glazes 🍰, and gelling agents.
Cold and Hot Chain: What Records to Keep for Compliance? ✅
You must record all food temperatures at each stage of processing, as well as at the start and end of delivery.
🔥 Hot Chain
In collective catering, the hot chain involves keeping food at a high temperature to ensure food safety. It is recommended to record:
- End-of-preparation temperatures (for cooking): the dish temperature must reach at least 63°C.
- Records before shipment and upon arrival:
- At departure ➡: product name, product temperature (≥63°C), quantity, departure time.
- At arrival ⬅: product name, product temperature (≥63°C), quantity, reception time.
❄️ Cold Chain: Temperature Monitoring
The cold chain consists of rapidly cooling food before storage and transport. The recommended records are:
- Cooling down records:
- Product name, time and temperature when placed in the cooling chamber.
- End time and temperature: the drop from 63°C to 10°C must happen within less than 2 hours.
- Transport records:
- At departure ➡: product name, product temperature (≤3°C), quantity, departure time.
- At arrival ⬅: product name, product temperature (≤3°C), quantity, reception time.
Digitize your records for better traceability! The Octopus HACCP app allows you to monitor the temperature of your preparations at every stage of production and during delivery.
What is the protocol for reheating in the cold chain? 🔥❄️
Upon receipt of a product in the cold chain at a satellite site, you must ensure the conformity of the reception. The elements to record are: product name, quantity, temperature 🌡️, and reception time.
Storage 🧊: any product received in the cold chain must then be stored at a temperature below 3 °C.
Reheating must be done quickly to reach 63 °C within one hour. It is therefore recommended to record the product name, start time and temperature, then the end time and temperature.
Service temperatures (for cold and hot products)
Cold chain in central kitchens: how to go digital?
Do you manage delivery rounds to several satellite sites, whether integrated or external to your organization? Octopus HACCP 🐙 can help you guarantee food safety for your cold and hot chains, directly on your HACCP tablet!
Our module dedicated to cold and hot chains allows you to perform all your HACCP checks during dispatch and receipt. Customizable to your specific logging habits, our HACCP software adapts perfectly to your needs.
Hot chain in nursing homes / EHPAD and home delivery: ensuring food safety with Octopus HACCP
Home delivery requires perfect food safety guarantees. At Octopus HACCP, we understand your specific requirements. Our module dedicated to HACCP logging for home delivery enables you to manage all your hot chain deliveries, ensuring control of both the cold and hot chains.
Ensure Food Safety During Your Deliveries
The Octopus HACCP app allows you to easily track your products at all your delivery points. 🐙
Record them at the central kitchen departure, and your satellite sites only need to validate the temperature 🥶 upon receipt.
The Octopus HACCP app is used by many organizations and supports them daily.
What is Hot Chain (Liaison Chaude)?
The hot chain refers to all hot food productions delivered with the temperature maintained above 63 °C. 🔥
Thus, from the end of production, through storage and delivery, until service, the temperature remains > 63 °C. That is why hot chains involve short transport times, mainly for retirement homes. This is also called home delivery. 🏠 However, central kitchens can also deliver to nearby satellite sites such as schools.
What are the different stages of the “liaison chaude” process?
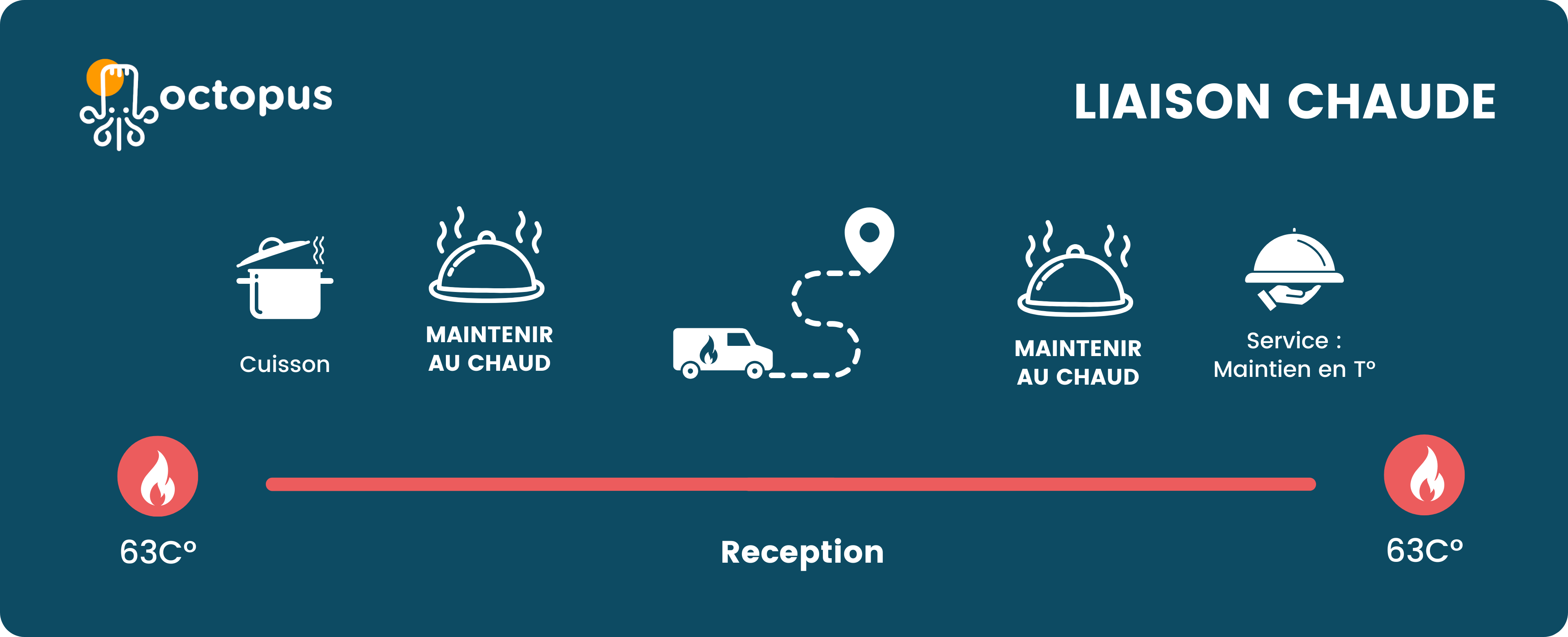
Hot link regulation: what does the law say? ⚖️
Food products must be transported in insulated vehicles that ensure maintenance of the temperature at +63 °C (decree n°2007-1791).
Product Shelf Life: What Does the Law Say?
For unpackaged products then repackaged, the use-by date cannot exceed the initial shelf life of the product or the component with the shortest shelf life.”
Download Your Cold and Hot Chain Guide in PDF
Fill out the form to receive a complete guide on cold and hot chains!





