Master rapid cooling in your restaurant!
Température
⏳ Temps de lecture : 5 min
? Mis à jour le : 25/02/2025
Rapid Cooling: Comply with the HACCP Method in Your Restaurant ?
Do you perform rapid cooling in your kitchen? Looking for more information on this critical step? In this article, we will cover: what the regulations say about rapid cooling, the different ways to perform rapid cooling, what information to keep, and more. At the end of this article, we offer you a rapid cooling chart to help you record your HACCP logs more easily.
What does the regulation say about rapid cooling? ?
Rapid cooling applies to hot prepared dishes that need to be cooled for storage in your cold rooms. To comply with the law and HACCP method, you must respect the time/temperature combination and cool from 63 °C to 3 °C in less than two hours. ⏳
Once rapid cooling is complete, you must store your food in a cold room at a maximum of 3 °C.
✏️ Note that: The two-hour countdown starts from the moment your product reaches 63 °C. For example, if your preparation is at 80 °C, the two-hour rapid cooling period only begins once it reaches 63 °C.
Why perform rapid cooling in a restaurant? ❄️
- For hygiene reasons: the risk of microbiological growth is very high between 63 °C and 10 °C. The vast majority of pathogenic bacteria are killed above 63 °C. Below 3 °C, their growth is greatly slowed down. ? If the product spends too much time in this temperature range (between 10 °C and 63 °C) and cools too slowly, bacterial multiplication and contamination risks are highest. It is therefore important to pass through this temperature range as quickly as possible. ⏳
- For organoleptic reasons: rapidly cooling a preparation helps preserve its organoleptic qualities better. There is less water evaporation, less oxidation, etc. This technique is especially essential in pastry for setting mousses, glazes, or gels.
How to integrate rapid cooling into my sanitary control plan? ❄️
The Sanitary Control Plan (SCP) is a mandatory document that describes the measures implemented by an establishment to guarantee food safety. Rapid cooling, being a critical step, must be clearly integrated into your SCP.
Rapid cooling is identified as a critical control point for food safety due to the risk of bacterial growth between 63 °C and 10 °C. To comply with regulations and especially to slow bacterial development, you must respect the critical limit of 2 hours and define corrective actions in case of non-compliance.
To follow the Good Hygiene Practices (GBPH), you need to specify the methods used (blast chiller, ice bath, portioning, etc.) and hygiene measures (use of clean containers, handling food with gloves, preventing cross-contamination). ✅
To ensure proper traceability of temperatures and prove compliance with HACCP standards, you must record your cooling logs. To assist you with this process, we offer at the end of the article a chart to track your rapid cooling. ?
You should also define corrective actions to prevent any non-compliance.
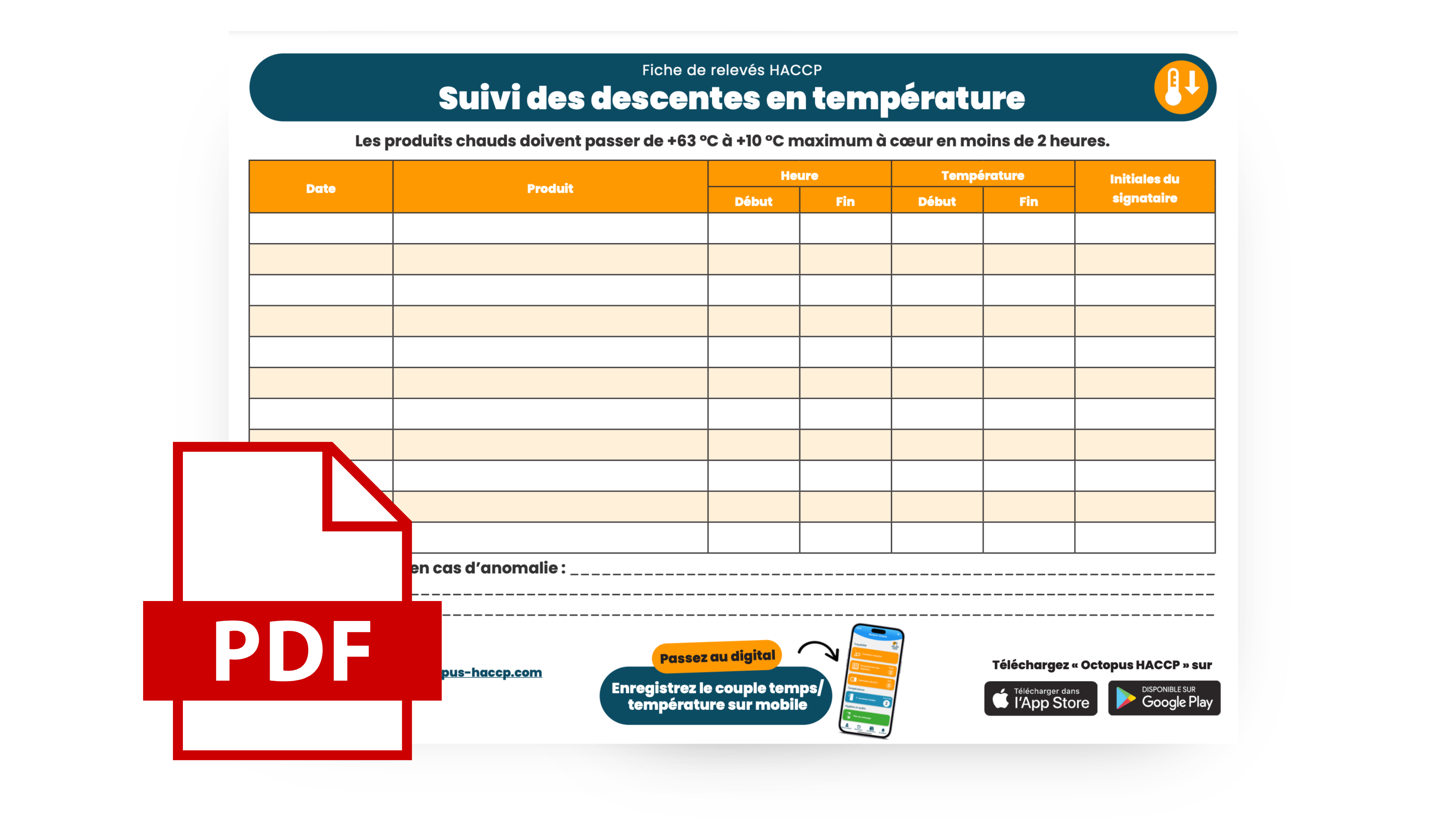
What information should be recorded for rapid cooling? ?
In practice, you must record the following for each cooled product:
- The name of the product,
- The time ? when cooling starts,
- The starting temperature, ?
- When the product is cooled below 10 °C: the cooling duration (< 2 hours),
- The end temperature of the cooling process.
What to do in case of non-compliance? ?
If the cooling is too slow:
- Check the proper functioning of the cooling equipment.
- Divide portions to speed up the cooling process.
If the time/temperature limit has been exceeded, you must record the corrective action.
You have several options:
- Consume within one hour: Even if you fail to cool your food within 2 hours, you can still consume it, but within one hour. Most bacteria will not have time to develop during this period, so it does not represent a health risk. ?
- If you do not consume it within one hour, you must discard it, as these foodstuffs cannot be stored. ?️
How to perform rapid cooling? ?
Using a blast chiller ❄️
Rapid cooling from +63 °C to +10 °C in less than 2 hours is an obligation of result, not means. Blast chillers are particularly suited for this protocol, but they are not the only way to quickly and evenly cool preparations.
How to perform rapid cooling without a blast chiller?
Traditional methods exist to cool without a blast chiller: ❄️
- Cooling under running cold water ? : pasta, rice, cooked vegetables ? in water: you can cool them under running cold water, then place them in containers and store in the cold room.
- Cooling in a container on a bed of ice ? : place the preparations in thin layers (the thinner the layer, the faster the cooling time). They should be placed on a bed of ice. When steam emission stops, the containers can be stored in the cold room.
- Cooling vacuum-packed pouches on a bed of ice or under running cold water : after vacuum packing, you can place the pouches either on a bed of ice or under running cold water before storage in the cold room.
In all cases, you must record the information ? for each product related to the time/temperature couple. This information will be requested during a hygiene inspection. ?
Finally, don’t forget to properly label your products after cooling if they are not intended for immediate consumption. So, product name, preparation date, expiration date.
In the absence of microbiological analysis, the maximum shelf life of a preparation is 3 days.
Regarding your control dishes, you can cool them in an ice bath or in a blast chiller, if available.
We advise against cooling your control dishes under a running water stream, as depending on the container’s seal, water infiltration could occur and damage your sample.
Download Your Rapid Cooling Log Sheet in PDF ?
This sheet allows you to record all your rapid cooling temperature logs.
You can download it for free in PDF format and print it. To receive it, please fill out the form below.





