Comprendre la méthode HACCP (enfin!)
Comprendre l’HACCP
⏳ Temps de lecture : 8 min
🗓 Mis à jour le : 17/07/2024
Sommaire
- Que veut dire méthode HACCP ?
- Qu’est-ce que la méthode HACCP ?
- Que dit la loi française ?
- Comment mettre la méthode HACCP en place dans mon établissement ?
- La traçabilité
- Comment effectuer un contrôle à réception ?
- Comment mettre en place la traçabilité interne ?
- Comment mettre en place la traçabilité secondaire ?
- Garantir la chaîne du froid
HACCP signifie Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point. En français, cela se traduit par système d’analyse des dangers et points critiques pour leur maîtrise. 🔎
Parler de norme HACCP n’est pas exact. Il ne s’agit pas d’une norme au sens français du terme. Les expressions : méthode HACCP, démarche HACCP, système HACCP sont plus appropriées.
Le saviez-vous ? 💡
Elle a été mise au point par la NASA 🚀 dans le cadre du programme spatial Apollo 👩🚀 afin de prévenir et d’éliminer au maximum tout danger biologique, chimique ou physique pour les astronautes. Quitte à déjeuner sur la lune, autant que la sécurité alimentaire soit parfaitement maîtrisée ! 🌠
Vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur la définition de la méthode HACCP ?
Alors, allons-y !
Qu’est-ce que la méthode HACCP ? 📒
La méthode HACCP repose sur l’identification, l’évaluation et la description des mesures de maîtrise. Elle repose sur 7 grands principes. 📃
- Analyse des dangers. 🔎
- Détermination des points critiques pour la maîtrise (les fameux CCP : Critical Control Point).
- Fixation du ou des seuil(s) critiques. 🛑
- Mise en place d’un système de surveillance des mesures de maîtrise des dangers aux CCP.
- Détermination des actions correctives à mettre en œuvre lorsque qu’un CCP donné est défaillant.
- Application des procédures de vérification afin de confirmer que le système HACCP fonctionne efficacement. ✅
- Constituer un dossier dans lequel figurent toutes les procédures et tous les relevés concernant ces principes et leur mise en application (traçabilité).
La méthode HACCP permet donc, via ces 7 principes, une vigilance par l’identification des étapes où il existe un danger de contamination.

La méthode HACCP peut être digitalisée 📳
Vous avez besoin d’aide pour bien mettre en place la méthode HACCP dans votre établissement ?
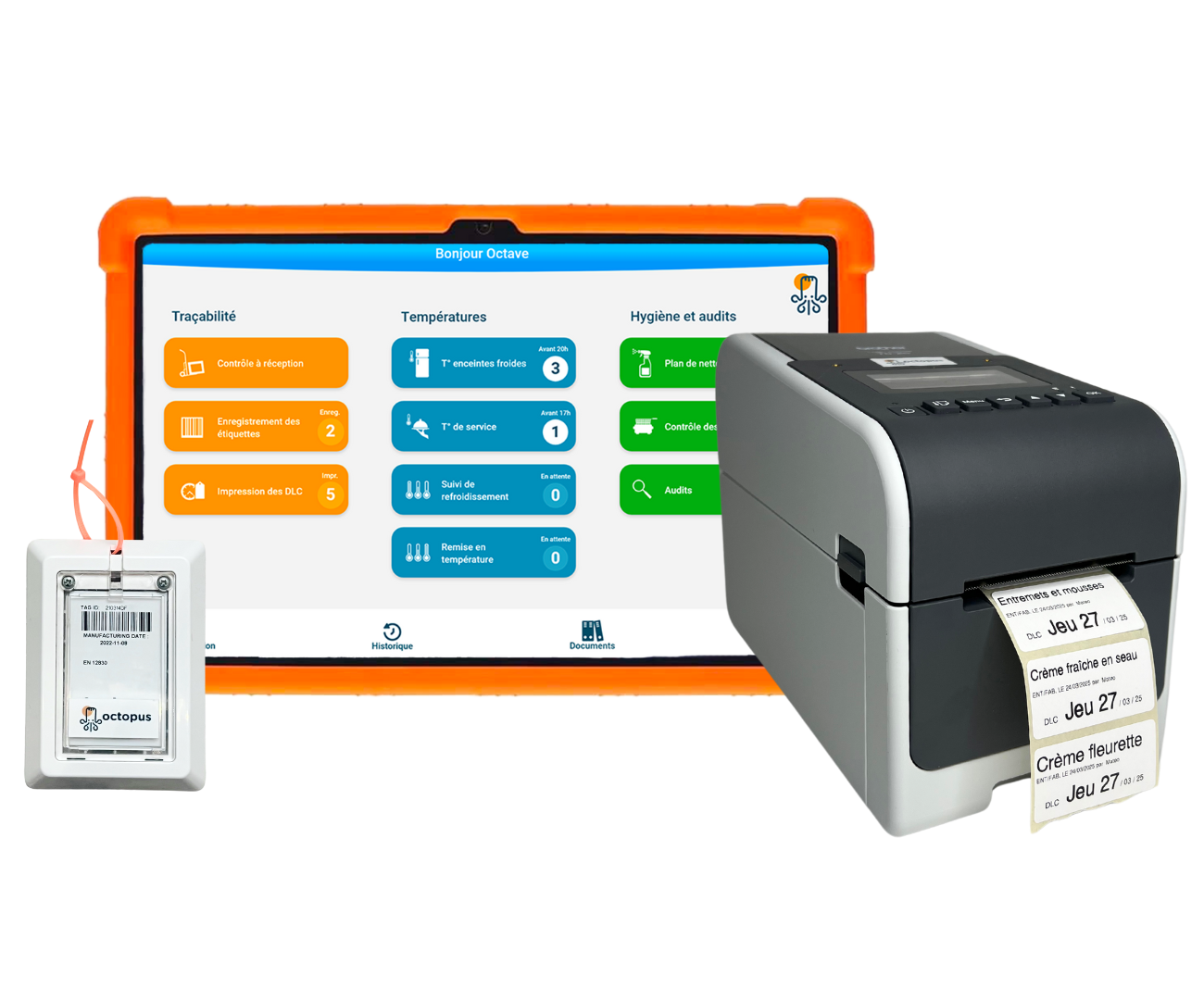
Avec l’application Octopus HACCP, vous êtes accompagné pour bien réaliser vos relevés HACCP au quotidien. Vous n’oubliez rien pour bien sauvegarder votre traçabilité 📸, vos températures ❄️ et votre plan de nettoyage ✨ : vous êtes en conformité avec la réglementation.
Que dit la loi française ? ⚖️
Depuis le 1er janvier 2006 : le « Paquet hygiène » s’applique à toute la filière agroalimentaire de la production, en passant par la transformation et jusqu’à la distribution au consommateur final. Ainsi, elle concerne tous les établissements de restauration et les métiers de bouche.
📃 Textes de référence :
- Règlement (CE) n°178/2002 est le texte clé édictant les grands principes du Paquet Hygiène. Il s’applique à tous les acteurs des filières alimentaires. Ce règlement assigne la responsabilité de la sécurité des denrées aux professionnels qui les placent sur le marché. Ainsi, il définit notamment des obligations de traçabilité 🔎, et de retrait de produits susceptibles de présenter un risque pour les consommateurs, etc.
- L’hygiène des aliments régie par le Règlement (CE) n°852/2004 est applicable à tous les exploitants du secteur alimentaire. Il exige entre autres, la mise en place de procédures fondées sur les principes HACCP dans le cadre d’un plan de maîtrise sanitaire,
- Règles spécifiques d’hygiène applicables aux denrées alimentaires d’origine animale 🥩 (Règlement (CE) n°853/2004) pour tous les exploitants du secteur alimentaire manipulant ou transformant des denrées animales ou d’origine animale. Il précise l’obligation d’agrément sanitaire.
D’autres règlements d’application ainsi que des arrêtés ministériels, viennent compléter cette liste non exhaustive et peuvent-être consultés sur le site du gouvernement.
Comment mettre la méthode HACCP en place dans mon établissement ? ✅
Si vous n’avez pas de Plan de Maitrise Sanitaire (PMS) vous devez au moins garantir la traçabilité de vos produits, respecter les DLC et DDM de vos produits, assurer le respect de la chaine du froid ou mettre en place un plan de nettoyage et de désinfection efficace.
Découvrez tous nos guides complets et gratuits pour vous aider à mieux maîtriser les bases de l’HACCP
La traçabilité 🔎
Pour assurer les essentiels d’une sécurité alimentaire maîtrisée vous devez entre autres garantir la traçabilité. Car tous les restaurants ont une obligation de traçabilité HACCP. 📃
Cette obligation est régie par le Règlement CE 178/2002 du 28 janvier 2002 qui fixe les procédures relatives à la sécurité des denrées alimentaires. La traçabilité alimentaire est le 7° et dernier pilier du Plan de Maitrise Sanitaire (PMS). 🧽️
Assurer la traçabilité alimentaire c’est être capable « de retracer, à travers toutes les étapes de la production, de la transformation et de la distribution, le cheminement d’une denrée alimentaire, d’un aliment pour animaux, d’un animal producteur de denrées alimentaires ou d’une substance destinée à être incorporée ou susceptible d’être incorporée dans une denrée alimentaire ou un aliment pour animaux ». 🔎
Pour assurer la traçabilité alimentaire, nous vous recommandons de suivre entre autre ces étapes :
- Traçabilité amont : assurer un contrôle à réception
- Traçabilité interne : conserver les n° de lot et les DLC de tous les produits sensibles que vous utilisez.
- Traçabilité secondaire : étiqueter tous vos produits entamés ou fabriqués qui retournent en chambre froide.
Vous souhaitez apprendre plus sur le sujet, découvrez notre guide gratuit sur la traçabilité.
Comment effectuer un contrôle à réception ? 📦
Concrètement, vous devez contrôler les marchandises que vous réceptionnez de vos distributeurs. Vous devez vérifier que les marchandises sont conformes. C’est-à-dire qu’aucun produit périmé ne vous a été livré et que les emballages sont intègres (pas de poches percées, de conserves abimées…). Mais vous devez aussi vérifier que la température de livraison est conforme. ❄️ Même en plein été par fortes chaleurs un produit frais doit vous être livré à 4°C maximum ! Dans le cas contraire vous devez refuser la marchandise.
Pour réaliser un contrôle à réception correct, vous devez vérifier avec un thermomètre la température du camion de livraison, puis réaliser un échantillonnage sur un produit sensible et noter sa température ainsi que sa DLC ou DDM.
Si lors de la livraison un produit n’est pas à bonne température (par exemple un steak haché livré à 5°C) ou que la DLC est passée ou trop courte, vous devez refuser la marchandise. 🚫
Comment mettre en place la traçabilité interne ? 🔎
Par exemple ✏️ : Pour garantir la traçabilité interne vous devez, entre autres, conserver entre autre les DLC ou DDM de vos produits et conserver les numéros de lots.
Pour chaque produit que vous déconditionnez vous devez conserver les informations figurant sur l’étiquette (pour les produits qui en sont pourvus), c’est-à-dire :
- Le nom du produit pour pouvoir l’identifier,
- La DLC (Date limite de consommation) ou DDM (Date de Durabilité Minimale, nouvelle appellation de la DLUO),
- Le numéro de lot,
- Pour les produits qui en sont pourvus (les viandes par exemple) : l’estampille sanitaire.
Comment conserver ces informations ? Soit en découpant et stockant vos étiquettes pendant au moins 6 mois, soit en les prenant en photo. 📷
Avec l’application Octopus HACCP, vos photos sont triées automatiquement et conservées sur nos serveurs sécurisés, vous n’avez donc plus besoin de découper et stocker vos étiquettes de traçabilité.
En cas de contrôle d’hygiène, avec notre logiciel haccp vous pouvez retrouver vos étiquettes en 2 clics ! ✅
Comment mettre en place la traçabilité secondaire ?
Vous devez aussi définir des DLC secondaires adaptées aux conditions de production et aux produits pour réduire le danger bactériologique 🧫️. Il est donc important d’établir des DLC secondaires adaptées pour chaque famille de produits dans votre cuisine, selon vos conditions de production.
Les DLC secondaires concernent toutes les denrées déconditionnées ou entamées. Ces denrées doivent être conservées à l’abri des contaminations extérieures (humidité, air, odeurs) soit dans des bacs filmés, soit fermés hermétiquement.🛡
Les produits frais doivent être conservés après déconditionnement à température conforme. Soit pour la majorité des cas, au frigo à une température inférieure à 4 °C pour éviter le développement et la prolifération de bactéries ou micro-organismes. ❄️
La durée de conservation dépend de vos conditions de production (port de gants, production dans un espace réfrigéré etc.). mais ne doit pas dépasser les 3 jours, si vous ne réalisez pas d’analyse microbiologique. En dessous de 3 jours, vous ne prenez pas de risque d’un point de vue réglementaire, mais certains produits ne peuvent pas se conserver 3 jours (comme le lait ou l’oeuf liquide, etc.). Au delà, vous devez effectuer des tests microbiologiques pour garantir la sécurité sanitaire des produits. Dans tous les cas vous devez dater vos produits entamés ou fabriqués de la date du jour de production/fabrication et de la date de péremption. 📅
Suivez-nous sur les réseaux sociaux 🔔
Nos experts partagent chaque semaine des conseils pratiques, des tutos et des décryptages clairs sur la réglementation HACCP. Rejoignez la communauté sur Linkedin, Facebook ou Instagram et Youtube.
Contrôle des températures 🌡️
Garantir la chaîne du froid ❄️
Pour garantir que la chaîne du froid n’est pas interrompue vous devez relever régulièrement avec un thermomètre la température de vos chambres froides et congélateurs ❄️. Il est conseillé de le faire au moins une fois par jour le matin avant d’attaquer la mise en place du jour. En cas de dépassement de température (seuil critique) vous devez noter votre action corrective (par exemple : destruction de marchandise).
Vous souhaitez apprendre plus sur le sujet, découvrez notre guide gratuit sur les températures.
L‘application Octopus HACCP permet de réaliser vos relevés de température. Le module est personnalisé avec vos frigos et congélateurs. Chaque jour, en un 1 clic, sauvegardez la température de ces derniers. ❄️
Vous pouvez aussi choisir de vous équiper d’enregistreurs de températures connectés qui feront les relevés à votre place et vous alertent en cas de problème. 📳
Les refroidissements rapides ⏳
Si vous êtes équipé d’une cellule de refroidissement, lorsque vous refroidissez un produit, vous devez noter l’heure et la température de départ, ainsi que la durée de refroidissement.
Cette durée ne doit pas excéder pour un produit chaud, 2 heures pour passer de 63 °C à 10 °C.
Car c’est dans cette intervalle de température que le risque de développement bactériologique est le plus grand. En refroidissement rapidement vos préparations vous garantissez la sécurité alimentaire. ✅
Présentation des denrées en buffets 🍴
Enfin, si vous servez de la nourriture en buffets vous devez garantir que la température de service est supérieure à 63 °C pour les plats chauds et inférieure à 5°C pour les produits froids, avec certaines exceptions comme pour le poisson cru (2°C).
Les charcuteries, poissons crus ou produits laitiers sont particulièrement sensibles, il convient de s’assurer que vos vitrines froides ou vos buffets sont à bonne température ! 🐟
Il est conseillé d’effectuer un relevé de température sur chaque catégorie de produits en privilégiant les produits sensibles, en début et fin de service. 🥦
Liaison froide ou liaison chaude 🌡
Dans le cas ou votre établissement effectue du portage à domicile en liaison chaude ou livre des satellites en liaison froide, la méthode HACCP s’applique scrupuleusement.
Pour garantir la sécurité alimentaire la chaîne du chaud ou la chaîne du froid doit être parfaitement respectée.
Par exemple ✏️ : En liaison chaude le produit doit être maintenu à plus de 63 °C en continu dès la fin de la production, durant le stockage et la livraison, jusqu’au service.
Pour la liaison froide, le refroidissement rapide, le stockage, le transport, et la remise en température doivent aussi scrupuleusement respecter la méthode HACCP. Pour en savoir plus sur la loi encadrant cette pratique consultez notre article détaillé sur la liaison froide et la liaison chaude.
Pour tous vos relevés de température, l’application Octopus HACCP possède une solution dédiée, vous pouvez tester l’application en cliquant sur le bouton ci-dessous.
Vous souhaitez apprendre sur le sujet, découvrez notre guide complet et gratuit sur les liaisons chaudes et froides
Le plan de nettoyage et de désinfection 🧽
L’hygiène en cuisine est une priorité pour garantir la sécurité alimentaire. Pour cela, vous devez avoir un plan de nettoyage clair et structuré ! Ce plan précise les différentes procédures concernant les surfaces, les équipements, les ustensiles, les fréquences, la méthode utilisée ainsi que les produits à utiliser. 🧼
Une fois votre plan de nettoyage mis en place, vous devez consigner vos relevés pour être conforme aux exigences sanitaires. Vous devez noter :
- La date et l’heure du nettoyage,
- L’élément concerné (plan de travail, frigos, sols…),
- Le produit utilisé,
- La personne en charge.
Ce suivi permet non seulement de s’assurer que toutes les tâches sont bien effectuées, mais aussi de prouver la conformité sanitaire de votre cuisine en cas de contrôle. 🔎
Les produits d’hygiène 🫧
Chaque produit d’entretien doit être documenté avec ses fiches techniques et fiches de données de sécurité (FDS). Ces documents précisent les conditions d’utilisation, les dosages et les précautions à prendre pour éviter tout danger. Vous devez les garder accessibles à votre personnel, pour qu’il puisse les consulter en cas de besoin. ✅
Digitalisez votre plan de nettoyage 📱
Pour faciliter vos relevés et gagner du temps, vous pouvez digitaliser votre plan de nettoyage et l’ensemble de vos relevés HACCP. Avec Octopus HACCP, vous pouvez créer un plan de nettoyage sur mesure, avec des checklists personnalisées. En quelques clics, cochez les actions effectuées et suivez celles restantes. Centralisez tous vos documents dans l’application : PMS, fiches techniques, fiches de données de sécurité, etc. 🚀
Maîtrisez les bases de l’HACCP avec nos formations gratuites 🐙
Vous souhaitez vous former à l’HACCP mais vous ne savez pas par où commencer ? Nous vous proposons des formations gratuites animées par des experts de l’HACCP. Chaque mois, nous abordons un sujet différent : traçabilité, contrôle des températures, plan de nettoyage, etc. 📙
- Il suffit de s’inscrire à la thématique qui vous intéresse, c’est gratuit !
- Partagez l’information à vos équipes ou collègues pour qu’ils montent également en compétence et reste à jour sur la règlementation.
- Que vous soyez débutant ou confirmé, nos formations HACCP sont ouvertes à tous. Avec Octopus, vous et vos équipes pouvez vous former en continu. ✅
- Ce sont des ateliers en ligne, en petits groupes
- Nos experts et vous pendant 30 minutes environ
- Vous pouvez poser toutes vos questions.
On répond à vos questions ! 🧡
Est-ce que l’HACCP est obligatoire ?
L’application de la méthode HACCP est obligatoire dans tous les restaurants ou établissements manipulant des denrées alimentaires. C’est ce qui garantit l’hygiène et la sécurité. Son application est une obligation réglementaire depuis 2006. Vous avez une obligation de résultat et non de moyen. C’est-à-dire que vous devez, entre autre, mettre en place un système de traçabilité, contrôler la chaîne du froid ou du chaud, et garantir l’hygiène et la désinfection de votre établissement. Concernant les moyens, vous pouvez le faire sur papier, ou sur une application comme Octopus HACCP. C’est vous qui choisissez ! L’important est de le faire !
Qui délivre la certification HACCP ?
En tant que professionnel de la restauration vous avez de mettre en place la méthode HACCP dans votre établissement. Pour ce faire, vous avez besoin de désigner un référent HACCP. Votre référent HACCP doit être formé à l’HACCP. Pour cela 2 manières : soit il est détenteur d’un diplôme professionnel obtenu après 2006, de type CAP, BEP, BTS, Bac professionnel, soit il a suivi la formation HACCP obligatoire, auprès d’un organisme agréé, d’une durée de 14h.
Pour obtenir la liste des professionnels habilités à délivrer cette formation HACCP certifiante, nous vous conseillons de vous rapprocher de votre syndicat professionnel ou de votre chambre de commerce et d’industrie.
Comment identifier les dangers HACCP ?
L’identification des dangers HACCP implique une analyse minutieuse de chaque étape de la production alimentaire pour déterminer les points critiques où des dangers potentiels peuvent survenir. Cela inclut l’évaluation des risques biologiques, chimiques et physiques, tels que la contamination bactérienne, les allergènes et les corps étrangers. Les outils comme l’analyse des risques et des points critiques pour leur maîtrise (HACCP) et les bonnes pratiques de fabrication (BPF) sont souvent utilisés pour cette identification. La mise en place d’un Plan de Maîtrise Sanitaire (PMS) vous permet d’identifier les dangers HACCP.

Être tenu informé de l’actualité réglementaire concernant l’hygiène et la sécurité alimentaire, c’est important !
Nos experts partagent avec vous chaque semaine des conseils, des tutos, un éclairage sur la réglementation HACCP, et répondent à vos questions.
Suivez nous et rejoignez le Food Safety Club d’Octopus HACCP.